Sudipta N. Sinha - Research
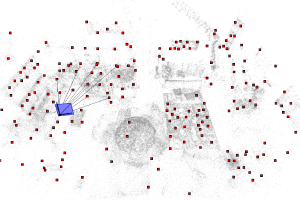 |
Learning to Detect Scene Landmarks for Camera Localization CVPR 2022 We present a new learned camera localization technique that eliminates the need to store features or a detailed 3D point cloud. Our key idea is to implicitly encode the appearance of a sparse yet salient set of 3D scene points into a convolutional neural network (CNN) that can detect these scene points in query images whenever they are visible. ... |
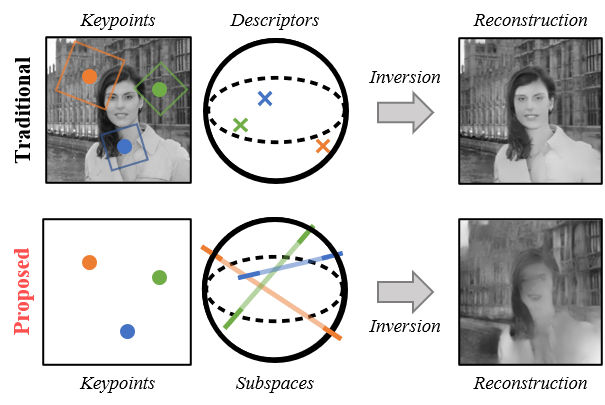 |
Privacy-Preserving Image Features via Adversarial Affine Subspace Embeddings CVPR 2021 Inversion of traditional local image features is a privacy concern in many applications. Our proposed approach obfuscates the appearance of the original image by lifting the descriptors to affine subspaces. Distance between the privacy-preserving subspaces enables efficient matching of features. The same concept can be applied to other domains such as face features for biometric authentication. ... |
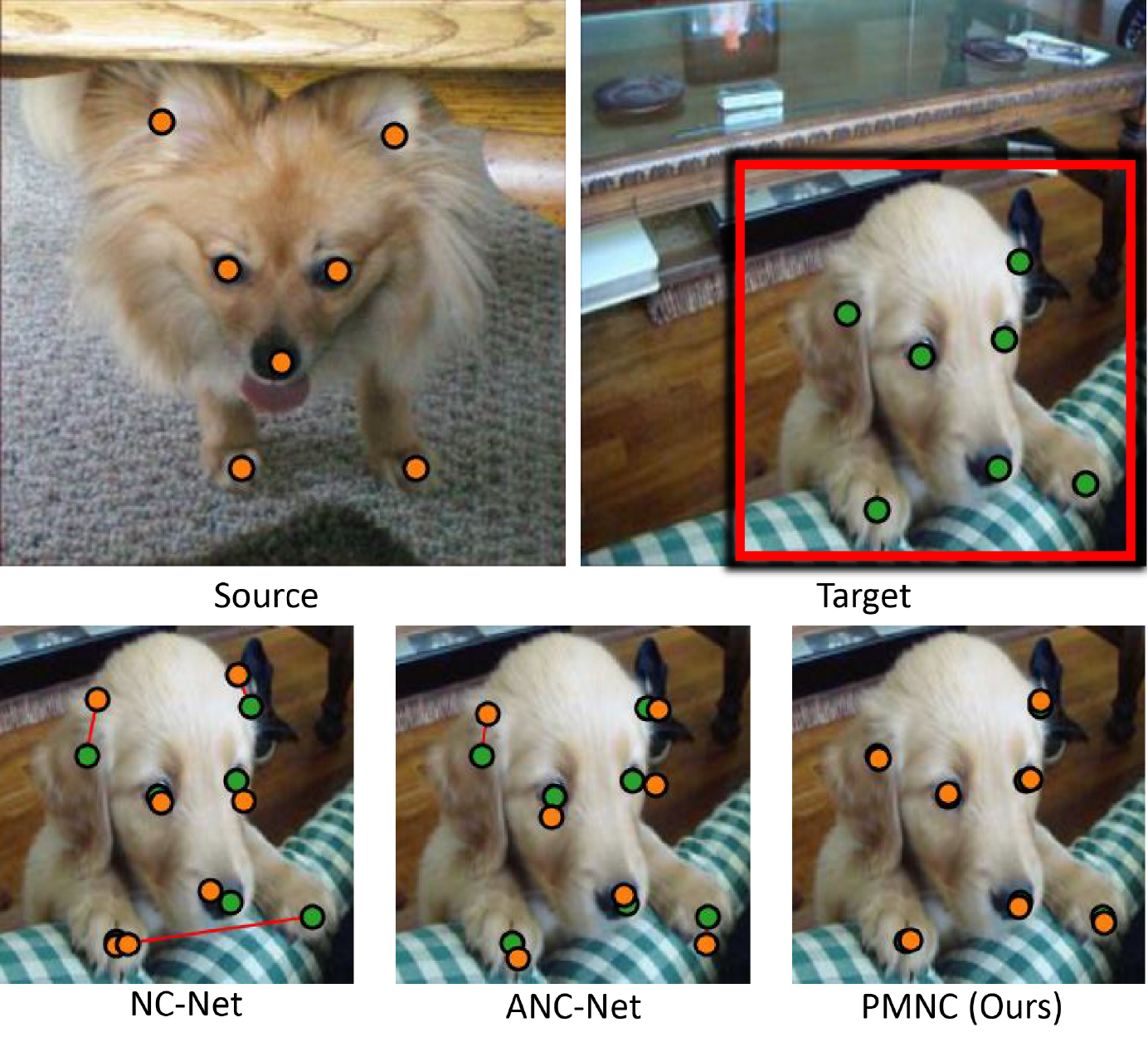 |
PatchMatch-Based Neighborhood Consensus for Semantic Correspondence CVPR 2021 We present a more efficient neighborhood consensus approach based on PatchMatch. For higher accuracy, we propose to use a learned local 4D scoring function for evaluating candidates during the PatchMatch iterations. We have devised an approach to jointly train the scoring function and the feature extraction modules by embedding them into a proxy model which is end-to-end differentiable. ... |
 |
Privacy Preserving Image Queries for Camera Localization ICCV 2019 We have developed a new 6-DoF camera localization technique that conceals the content of the query image when localization is performed in a cloud-based service. This is a follow up of our previous work on privacy preserving camera localization where we devised a way to conceal the 3D point cloud map which is used for localization. ... |
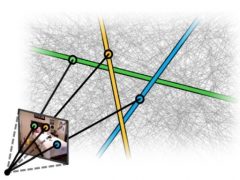 |
Privacy Preserving Image-Based Localization CVPR 2019 How can we avoid disclosing confidential information about the captured 3D scene, and yet allow reliable camera pose estimation? This paper proposes the first solution to what we call privacy preserving image-based localization using new ideas from geometry. ... |
 |
Inverting Structure from Motion Reconstructions CVPR 2019 We show, for the first time, that SfM point clouds and features retain enough information to reveal scene appearance and compromise privacy. We present a privacy attack that reconstructs color images of the scene. ... |
 |
Learning to Fuse Proposals in Semi-Global Matching
ECCV 2018 We propose SGM-Forest, an efficient extension to the SGM stereo matching algorithm, that uses a random decision forest classifier to fuse multiple disparity map proposals, each of which is obtained by solving an independent 1D scanline optimization problem. SGM-Forest is consistently more accurate than SGM and its performance generalize very well to new datasets. ... |
 |
Real-Time Seamless Single Shot 6D Object Pose Prediction CVPR 2018 We propose a single-shot approach for simultaneously detecting an object in an RGB image and predicting its 6D pose without requiring multiple stages or having to examine multiple hypotheses. Unlike a recently proposed single-shot technique for this task (Kehl et al. ICCV'17) that only predicts an approximate 6D pose that must then be refined, ours is accurate enough not to require additional post-processing ... |
 |
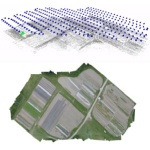
Submodular Trajectory Optimization for Aerial 3D Scanning ICCV 2017 Drones equipped with cameras are emerging as a powerful tool for large-scale aerial 3D scanning, but existing automatic flight planners do not exploit all available information about the scene, and can therefore produce inaccurate and incomplete 3D models. We present an automatic method to generate drone trajectories, such that the imagery acquired during the flight will later produce a high-fidelity 3D model. Our method uses a coarse estimate of the scene geometry to plan camera trajectories that: (1) cover the scene as thoroughly as possible; (2) encourage observations of scene geometry from a diverse set of viewing angles; (3) avoid obstacles; and (4) respect a user-specified flight time budget ... |
 |
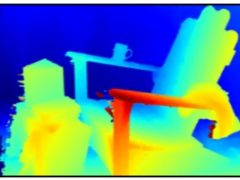
Fast Multi-frame Stereo Scene Flow with Motion Segmentation CVPR 2017 We propose a new multi-frame method for efficiently computing scene flow (dense depth and optical flow) and camera ego-motion for a dynamic scene observed from a moving stereo camera rig. Our technique also segments out moving objects from the rigid scene. In our method, we first estimate the disparity map and the 6-DOF camera motion using stereo matching and visual odometry. We then identify regions inconsistent with the estimated camera motion and compute per-pixel optical flow ... |
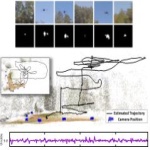 |
Flight Dynamics-based Recovery of a UAV Trajectory using Ground Cameras CVPR 2017 We propose a new method to estimate the 6-dof trajectory of a flying object such as a quadrotor UAV within a 3D airspace monitored using multiple fixed ground cameras. It is based on a new structure from motion formulation for the 3D reconstruction of a single moving point with known motion dynamics. Our main contribution is a new bundle adjustment procedure which in addition to optimizing the camera poses, regularizes the point trajectory using a prior based on motion dynamics (or specifically flight dynamics) ... |
 |
FarmBeats: An IoT Platform for Data-Driven Agriculture NSDI 2017 Data-driven techniques help boost agricultural productivity by increasing yields, reducing losses and cutting down input costs. However, these techniques have seen sparse adoption owing to high costs of manual data collection and limited connectivity solutions. In this paper, we present FarmBeats, an end-to-end IoT platform for agriculture that enables seamless data collection from various sensors, cameras and drones. FarmBeats’s system design that explicitly accounts for weather-related power and Internet outages ... |
 |
Robust Multiview Photometric Stereo using Planar Mesh Parameterization TPAMI 2017 We propose a robust uncalibrated multiview photometric stereo method for high quality 3D shape reconstruction. In our method, a coarse initial 3D mesh obtained using a multiview stereo method is projected onto a 2D planar domain using a planar mesh parameterization technique. We describe methods for surface normal estimation that work in the parameterized 2D space that jointly incorporates all geometric and photometric cues from multiple... |
 |
Multiview Rectification of Folded Documents TPAMI 2017 Digitally unwrapping images of paper sheets is crucial for accurate document scanning and text recognition. This paper presents a method for automatically rectifying curved or folded paper sheets from a few images captured from multiple viewpoints. Prior methods either need expensive 3D scanners or model deformable surfaces using over-simplified parametric representations. In contrast, our method uses regular images and is based on general developable surface models... |
 |
Efficient and Robust Color Consistency for Community Photo Collections CVPR 2016 We present an efficient technique to optimize color consistency of a collection of images depicting a common scene. Our method first recovers sparse pixel correspondences in the input images and stacks them into a matrix with many missing entries. We show that this matrix satisfies a rank two constraint under a simple color correction model. These parameters can be viewed as pseudo white balance and gamma correction parameters for each input image. We present a robust low-rank matrix factorization method... |
 |
Joint Recovery of Dense Correspondence and Cosegmentation in Two Images CVPR 2016 We propose a new technique to jointly recover cosegmentation and dense per-pixel correspondence in two images. Our method parameterizes the correspondence field using piecewise similarity transformations and recovers a mapping between the estimated common “foreground” regions in the two images allowing them to be precisely aligned. Our formulation is based on a hierarchical Markov random field model with segmentation and transformation labels. The hierarchical structure uses nested image regions to constrain inference... |
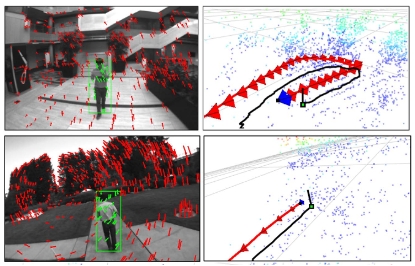 |
Monocular Localization of a moving person onboard a Quadrotor MAV ICRA 2015 In this paper, we propose a novel method to recover the 3D trajectory of a moving person from a monocular camera mounted on a quadrotor micro aerial vehicle (MAV). The key contribution is an integrated approach that simultaneously performs visual odometry (VO) and persistent tracking of a person automatically detected in the scene. All computation pertaining to VO, detection and tracking runs onboard the MAV from a front-facing monocular RGB camera... |
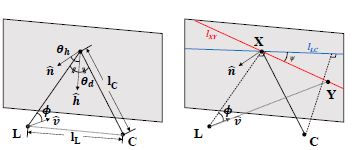 |
Calibrating a non-isotropic near point light source using a plane CVPR 2014 We show that a non-isotropic near point light source rigidly attached to a camera can be calibrated using multiple images of a weakly textured planar scene. Weprovethat if the radiant intensity distribution (RID) of a light source is radially symmetric with respect to its dominant direction, then the shading observed on a Lambertian scene plane is bilaterally symmetric with respect to a 2D line on the plane... |
 |
High-Resolution Stereo Matching using Local Plane Sweeps CVPR 2014 We present a stereo algorithm designed for speed and efficiency that uses local slanted plane sweeps to propose disparity hypotheses for a semi-global matching algorithm. Our local plane hypotheses are derived from initial sparse feature correspondences followed by an iterative clustering step. Local plane sweeps are then performed around each slanted plane to produce out-of-plane parallax and matching-cost estimates... |
 |
3D Spin Movies and Photosynth 2 2013 We propose a way to create more realistic transitions when moving from photograph to photograph, thereby providing an immersive viewing experience. Such transitions were made possible using computer-vision techniques to calculate the depth of each pixel for all the images in the collection. ... |
 |
Multiview Photometric Stereo using Planar Mesh Parameterization ICCV 2013 We propose a method for accurate 3D shape reconstruction using uncalibrated multiview photometric stereo. A coarse mesh reconstructed using multiview stereo is first parameterized using a planar mesh parameterization technique. Subsequently, multiview photometric stereo is performed in the 2D parameter domain of the mesh, where all geometric and photometric cues from multiple images can be treated uniformly ... |
 |
Leveraging Structure from Motion to Learn Discriminative Codebooks for Scalable Landmark Classification CVPR 2013 In this paper we propose a new technique for learning a discriminative codebook for local feature descriptors, specifically designed for scalable landmark classification. The key contribution lies in exploiting the knowledge of correspondences within sets of feature descriptors during codebook learning. Feature correspondences are obtained using structure from motion (SfM) computation on Internet photo collections ... |
 |
Detecting and Reconstructing 3D Mirror Symmetric Objects ECCV 2012 We present a system that detects 3D mirror-symmetric objects in images and then reconstructs their visible symmetric parts. Our detection stage is based on matching mirror symmetric feature points and descriptors and then estimating the symmetry direction using RANSAC. We enhance this step by augmenting feature descriptors with their affine deformed versions and matching these extended sets of descriptors... |
 |
Multiple View Object Cosegmentation using Appearance and Stereo Cues ECCV 2012 We present an automatic approach to segment an object in calibrated images acquired from multiple viewpoints. Our system starts with a new piecewise planar layer-based stereo algorithm that estimates a dense depth map that consists of a set of 3D planar surfaces. The algorithm is formulated using an energy minimization framework that combines stereo and appearance cues, where for each surface... |
 |
Real-time Image-based 6-DOF Localization in Large-Scale Environments CVPR 2012 We present a real-time approach for image-based localization within large scenes that have been reconstructed offline using structure from motion (Sfm). From monocular video, our method continuously computes a precise 6-DOF camera pose, by efficiently tracking natural features and matching them to 3D points in the Sfm point cloud. Our main contribution lies in efficiently interleaving a fast keypoint tracker that uses inexpensive binary feature descriptors with a new approach for direct 2D-to-3D matching... |
 |
Discovering and Exploiting 3D Symmetries in Structure from Motion
CVPR 2012 Many architectural scenes contain symmetric or repeated structures, which can generate erroneous image correspondences during structure from motion (Sfm) computation. Prior work has shown that the detection and removal of these incorrect matches is crucial for accurate and robust recovery of scene structure. In this paper, we point out that these incorrect matches, in fact, provide strong cues to the existence of symmetries and structural regularities in the unknown 3D structure... |
 |
Image-Based Rendering for Scenes with Reflections SIGGRAPH 2012 We present a system for image-based modeling and rendering of real-world scenes containing reflective and glossy surfaces. Previous approaches to image-based rendering assume that the scene can be approximated by 3D proxies that enable view interpolation using traditional back-to-front or z-buffer compositing. In this work, we show how these can be generalized to multiple layers that are combined in an additive fashion to model the reflection and transmission of light... |
 |
Structure from motion for scenes with large duplicate structures CVPR 2011 Most existing structure from motion (SFM) approaches for unordered images cannot handle multiple instances of the same structure in the scene. When image pairs containing different instances are matched based on visual similarity, the pairwise geometric relations as well as the correspondences inferred from such pairs are erroneous, which can lead to catastrophic failures in the reconstruction... |
 |
A Multi-Stage Linear Approach to Structure from Motion ECCV 2010 workshop We present a new structure from motion (Sfm) technique based on point and vanishing point (VP) matches in images. First, all global camera rotations are computed from VP matches as well as relative rotation estimates obtained from pairwise image matches. A new multi-staged linear technique is then used to estimate all camera translations and 3D points simultaneously... |
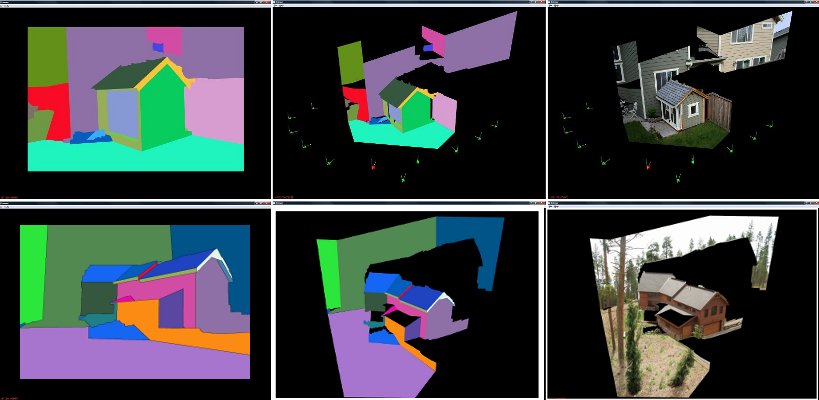 |
Piecewise Planar Stereo for Image-based Rendering ICCV 2009 We present a novel multi-view stereo method designed for image-based rendering that generates piecewise planar depth maps from an unordered collection of photographs. First a discrete set of 3D plane candidates are computed based on a sparse point cloud of the scene (recovered by structure from motion) and sparse 3D line segments reconstructed from multiple views... |
 |
Interactive 3D Architectural Modeling from Unordered Photo Collections SIGGRAPH Asia 2008 We present an interactive system for generating photorealistic, textured, piecewise-planar 3D models of architectural structures and urban scenes from unordered sets of photographs. To reconstruct 3D geometry in our system, the user draws outlines overlaid on 2D photographs. The 3D structure is then automatically computed by combining the 2D interaction with the multi-view geometric information recovered by performing structure from motion analysis on the input photographs... |